Search Suggestions
Categories
Products
View All Results
Search Suggestions
Categories
Products
View All Results
Without spark plugs, most petrol-powered vehicles won't start or move. Engines rely directly on spark plugs to perform, and so defective spark plugs can lead to significant problems in your vehicle, such as prolonged cold-starting and misfires during acceleration.
If your vehicle doesn't have healthy, functional spark plugs, it won't be able to perform at the correct capacity and you might also see a drop in fuel economy. So, discover exactly what spark plugs are, how they work, and how to replace them in our comprehensive guide.
Spark plugs are fundamental components in a petrol-powered vehicle's engine. Their primary task is to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber, an essential process for the engine's power generation. This ignition is achieved through the delivery of an electrical spark by each spark plug, effectively initiating combustion and enabling the engine to operate.
The efficiency of internal combustion engines heavily relies on the precision of the spark plugs. The timing and strength of the spark are critical; it must occur at exactly the right moment to ensure efficient combustion. Inadequately timed or weak sparks can lead to a host of engine problems, including reduced fuel efficiency and increased emissions.
Spark plugs also serve a vital role beyond ignition. They are instrumental in transferring heat away from the combustion chamber. The operating temperature of a spark plug can reveal various engine conditions, making them indispensable not only for engine operation but also as diagnostic tools. Mechanics can assess the health of an engine by examining used spark plugs and identifying issues such as engine overheating, pre-ignition, or imbalances in the fuel mixture.
Despite their modest size, spark plugs are designed to endure extreme conditions. They must handle high voltages, often exceeding 40,000 volts, and temperatures above 800°C. This challenging environment necessitates the use of robust materials in the construction of spark plugs, ensuring they can withstand such conditions while maintaining reliable performance.
The function of a spark plug in an engine is both fascinating and complex. At its core, a spark plug is an electrical device that is inserted into the cylinder head of an internal combustion engine. It plays a crucial role in igniting the air-fuel mixture within the engine's combustion chamber.
How does this process occur? The journey starts with a high-voltage current supplied by the ignition system. This current is directed to the spark plug's central electrode, which is insulated by a ceramic coating. The only path for this high voltage to reach the engine block, and hence complete the circuit, is by jumping across a small gap to the spark plug's ground electrode. This action creates a spark – a tiny but powerful electrical discharge – that ignites the air-fuel mixture. This ignition is what powers the engine.
The design of spark plugs includes several key components a central electrode - which often contains a copper core for better conductivity - and a ground electrode. These electrodes are separated by an air gap, where the spark occurs. The entire assembly is encased in a durable metal shell, which helps in dissipating heat and provides the necessary electrical grounding.
A spark plug's effectiveness is influenced by its construction and materials. For instance, the width of the electrode gap is crucial. If the gap is too narrow, the spark may be too weak, leading to inefficient fuel combustion. Conversely, a gap that is too wide may prevent the spark from occurring at all, leading to engine misfires.
Spark plugs come in various types, each distinguished by the materials used in their construction, which directly impacts their performance, durability, and suitability for different engine types.
Each type of spark plug has its specific advantages. For instance, copper plugs, despite their shorter lifespan, are often preferred in high-performance engines due to their superior conductivity. On the other hand, iridium and platinum plugs, while more expensive, offer greater longevity and are thus more cost-effective in the long run.
The choice of spark plug material should align with the vehicle's requirements. Factors like engine type, manufacturer's recommendations, and driving conditions play a crucial role in determining the most suitable spark plug type. It's essential to consult the vehicle's manual, a professional mechanic or us here at Opie Oils to ensure the right selection for optimal engine performance.
Recognising when to change spark plugs is essential for maintaining optimal engine performance. Several signs indicate it might be time to replace them:
Inspecting the spark plugs can provide further insights into their condition. Signs of wear include electrodes that are burnt away, deposits on the plug, or an altered electrode gap. These physical signs are indicators that the spark plugs are due for replacement.
Regular inspection and timely replacement of spark plugs are crucial for vehicle maintenance. It's advisable to follow the manufacturer's recommended schedule for spark plug replacement, but also to be aware of these signs as they can occur before the scheduled maintenance period.
Spark plugs become less effective at doing their job over time, because of wear or other system issues. They can become fouled because of combustion, overheating, contamination or losing their ability to spark the air-fuel mixture and dissipate heat away from the combustion chamber.
If they aren't replaced, the gap between the plug's electrodes widens, meaning the spark has to jump across a greater distance to trigger combustion. Eventually, the widening of the gap can lead to irregular or erratic combustion.
Diagnosing issues with spark plugs is an important aspect of vehicle maintenance. Understanding how to identify and address common spark plug problems can enhance engine performance and longevity. Here are key areas to focus on for spark plug fault-finding.
Inspecting the condition of spark plugs can reveal much about the engine's health. Look for signs like sooty (rich mixture) or white (lean mixture) deposits, or electrodes that are worn down. Each of these conditions can indicate different issues, such as an improper air-fuel mixture or engine overheating.

If the firing end of the spark plug is brown or light grey, the engine condition can be judged to be good and the spark plug is functioning correctly.

The gathering of different deposits on the firing end is influenced by oil leakage, fuel quality and engine operating period. The deposits can come from Carbon, Lead, Bromine, Calcium, Sulphur, Barium and Zinc.

Dry and Wet Fouling is another way the firing end can be damaged.
This occurs when the spark plug firing end does not reach the self-cleaning temperature, leading to carbon deposits on the insulator nose. It's often caused by a heat range that's too cold for the engine or by an excessively rich air-fuel mixture.
If the insulation resistance between the centre electrode and the "shell" is over 10M ohms the engine can start up normally. However, if the insulation resistance drops to zero, the firing end is fouled by either wet or dry carbon.

If your spark plug firing end looks yellowish brown on the insulator nose, this is found on spark plugs that have been damaged by lead. Also, this kind of damage cannot be detected by a resistance tester at room temperature. Lead compounds combines at different temperatures; those formed at 370-420 degrees Celsius have the biggest influence on the resistance.

If your spark plug has overheated, the insulator tip is glazed or glossy. Deposits which have gathered on the insulator tip have melted, and there is a chance that the insulator will have blistered. Spark plugs can overheat due to several reasons, such as using a heat range that's too hot, over-advanced ignition timing, or an excessively lean air-fuel mixture. Overheating can lead to pre-ignition and serious engine damage.

Breakage is normally caused by a thermal shock due to sudden heating or cooling – if you notice a breakage on your spark plug, replace it immediately.

A worn spark plug not only wastes fuel but also strains the whole ignition, this is because it requires a higher voltage. A worn spark plug can reduce the engine efficiency by reducing the fuel economy and increases the exhaust emissions. For your reference, the normal rate of gap growth is about 0.01 0.02mm/1,000 Km for four stroke engines and about 0.02 0.04mm/1,000 Km for two stroke engines.

Over time, the electrodes on a spark plug can wear down, changing the gap between them.
The electrodes have oxidised, and when the oxidation is heavy there will be green on the surface. The surfaces of the electrodes are also fretted and rough.
This altered gap can affect the spark quality, leading to misfires and reduced engine efficiency.

An Abnormal Erosion is caused by corrosion, oxidation or reaction with the lead. This results in abnormal gap growth. This altered gap can affect the spark quality, leading to misfires and reduced engine efficiency.

Lead Erosion is caused by the lead compounds in the petrol which react chemically with the material of the electrodes (nickel alloy) at high temperatures. Crystals of nickel alloy fall off because of the lead compounds permeating and separating the grain boundary of the nickel alloy. Typical lead erosion causes the surface of the electrode to become thinner and the tip of the electrode looks like it has been chipped.

If the firing end is melted, this means it has over heated. Mostly, this will result in the electrode surface being rather lustrous and uneven. Keep in mind, the melting point of nickel alloy is 1,200 – 1,300 degrees Celsius.
Physical damage to the spark plug, such as a cracked insulator or a damaged shell, can compromise its function. Such damage might occur due to over-tightening or impacts during installation or operation.
Regular inspection and understanding the signs of spark plug wear and damage are crucial. Correctly diagnosing and addressing these issues can prevent more significant engine problems and ensure optimal performance.
Replacing spark plugs is a critical maintenance task that can significantly improve engine performance and efficiency. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you replace your spark plugs.
Ensure the engine is cool before you start. Gather the necessary tools, including a spark plug socket, ratchet, and extension. It's also a good idea to have a piece of rubber hose that fits snugly over the top of the new spark plug to assist with installation.
Begin by locating the spark plugs, which are typically found on the top or side of the engine. Remove the spark plug wire by gently twisting and pulling the boot (not the wire). Use the spark plug socket and ratchet to unscrew the old spark plug with care, avoiding damage to the cylinder head threads because you do not want them to snap.
Examine the old spark plugs for signs of wear or damage, such as oil deposits, ash deposits, or electrode erosion. This can provide valuable information about the engine's condition and performance.
Check the gap on new spark plugs using a spark plug gapping tool to ensure it matches your vehicle's specifications. Screw in the new spark plug by hand to prevent cross-threading. Once hand-tight, use the spark plug socket and ratchet to tighten the spark plug to the manufacturer's recommended torque. Avoid over-tightening, as this can damage the plug or threads.
Once the new spark plugs are installed, reconnect the spark plug wires, ensuring a snug fit on the spark plug's terminal.
After replacing all the spark plugs, double-check your work to ensure all tools and materials are removed from the engine area. Start the engine to verify that it runs smoothly and there are no misfires or unusual noises.
Replacing spark plugs can be a straightforward process, but it requires diligence. If you're uncertain or uncomfortable performing this task, it's always best to consult a professional mechanic.
Cleaning spark plugs can extend their life and improve engine performance. Here's how you can clean your spark plugs effectively:
Remember, while cleaning can help extend the life of your spark plugs, it's not a substitute for replacing them when needed. Always follow your vehicle's maintenance schedule for spark plug replacement.
Selecting the right spark plug for your vehicle is essential for optimal engine performance and efficiency. Here are key factors to consider when choosing spark plugs:
By carefully selecting spark plugs that meet these criteria, you can ensure efficient combustion, reduced emissions, and optimal engine performance.
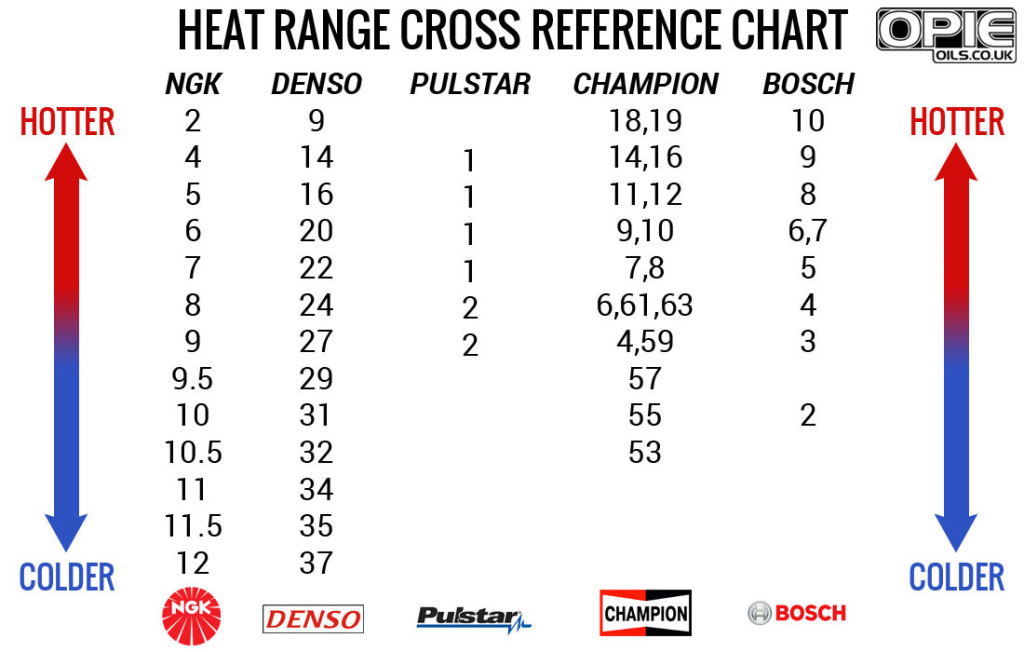
The heat rating of a spark plug refers to its ability to dissipate heat generated during the combustion process within the engine. Spark plug heat ranges are classified by numbers, with lower numbers usually indicating hotter plugs and higher numbers usually indicating colder plugs... but this changes from brand to brand! So, for example, a "hot" Bosch plug is a high number, and a "hot" NGK or Denso plug is a low number.
Colder Plugs have a greater ability to transfer heat away from the combustion chamber, making them suitable for engines that generate a lot of heat or run at high speeds for extended periods. Colder plugs help prevent pre-ignition or detonation in high-performance or turbocharged engines.
Hotter Plugs retain more heat within the combustion chamber, which can help prevent fouling in engines that operate at lower speeds or under lighter loads. Hotter plugs are typically used in older engines, engines with low compression ratios, or in colder climates to prevent fouling.
Selecting the appropriate heat range for spark plugs is crucial for engine performance, efficiency, and longevity. It can be a pain when you need a new spark plug but you don't know how your current heat range translate to a new brand, so we've created a heat range cross reference chart that shows comparisons between 5 major brands of spark plugs.
Can spark plugs increase horsepower?
Spark plugs themselves don't increase horsepower, but they can influence engine performance. High-quality spark plugs ensure efficient combustion, which can contribute to the optimal performance of your engine. However, any horsepower increase would be minimal and more related to restoring original performance rather than boosting it beyond factory specifications.
How often should spark plugs be changed in a vehicle?
The frequency of changing spark plugs varies depending on the vehicle and type of spark plug. Generally, copper spark plugs should be checked or replaced every 20,000 to 30,000 miles, while iridium or platinum plugs can last up to 60,000 to 100,000 miles. Always refer to your vehicle's owner manual for specific recommendations or check in with us.
Can bad spark plugs cause a check engine light to come on?
Yes, bad spark plugs can trigger the check engine light. If a spark plug is failing or has failed, it can cause misfires or irregular combustion, leading to an error code being sent to the vehicle's computer system, which in turn lights up the check engine light.
Are there different sizes of spark plugs?
Yes, spark plugs come in different sizes to fit various engines. The size mainly refers to the thread size and length of the spark plug. It's crucial to use the size specified for your vehicle to ensure proper fit and function. Use our online spark plug spark plug recommendation tool get the right plug for your car.
Can I clean spark plugs instead of replacing them?
While cleaning spark plugs can temporarily improve their function, it's often a short-term solution. If the plugs are heavily worn or damaged, cleaning won't restore their full functionality. Regular replacement according to the manufacturer's schedule is recommended for the best engine performance, and to be honest, standard spark plugs won't break the bank.
Is it worth paying more for expensive spark plugs?
Despite what some automotive stores may tell you, all spark plugs aren't the same.
Copper spark plugs, for example, have the shortest lifespan, while spark plugs made of durable materials like iridium can provide up to four times the lifespan of a copper one.
Spark plugs are small but mighty components that play a crucial role in the performance and health of your vehicle's engine.
From igniting the air-fuel mixture to providing insights into engine conditions, their importance cannot be overstated. Understanding the various aspects of spark plugs – from how they work, types available, and signs of wear, to maintenance practices – is key to ensuring your vehicle operates efficiently and reliably.
Regular maintenance, including cleaning and timely replacement of spark plugs, can significantly impact fuel efficiency, engine smoothness, and overall vehicle performance. Being mindful of the signs that indicate spark plug issues and knowing how to address them can save you from costly repairs and keep your vehicle running smoothly.
Choosing the right spark plugs for your vehicle, and considering factors such as manufacturer's recommendations, engine type, and spark plug materials, can make a substantial difference in engine performance. It's a balance of understanding what your vehicle needs and how different types of spark plugs can meet those needs.
In essence, spark plugs, though small, are pivotal in the grand scheme of engine functionality and efficiency. Regular checks, understanding their conditions, and proper maintenance can enhance your driving experience and prolong the life of your engine.
You can buy spark plugs for your vehicle at Opie Oils. We have a broad selection from the industry leaders - NGK, Bosch, DENSO, NAPA, Blue Print and more. Find the right spark plugs for your car with our online spark plug recommendation tool.
If you have questions, please do get in touch with our technical experts via phone, email or chat.